Conversational Queries: Democratizing Data Consumption with Generative AI
Abstract
This report defines conversational queries, why analytics and business teams should consider using them, and how they can do so.
Table of Contents
- Conversational Queries: Democratizing Data Consumption with Generative AI
- What are conversational queries?
- State of business intelligence
- How do conversational queries work?
- Why should companies consider conversational query tools?
- Use case
- Conclusion
Conversational Queries: Democratizing Data Consumption with Generative AI
Business managers must have facts at their fingertips to make smart decisions in competitive, dynamic markets. But those facts can be evasive. Rigid and outdated BI artifacts prevent business managers from locating, understanding, and sharing answers to their ad-hoc questions. Many of these managers cannot answer their own questions because budget constraints and organizational silos block their access to BI tools. Flying blind, they make decisions based on hunch and habit rather than hard evidence. In a March 2024 poll by BARC, only 26% of 42 data practitioners said business managers in their organization get the operational facts they need from BI reports and dashboards.
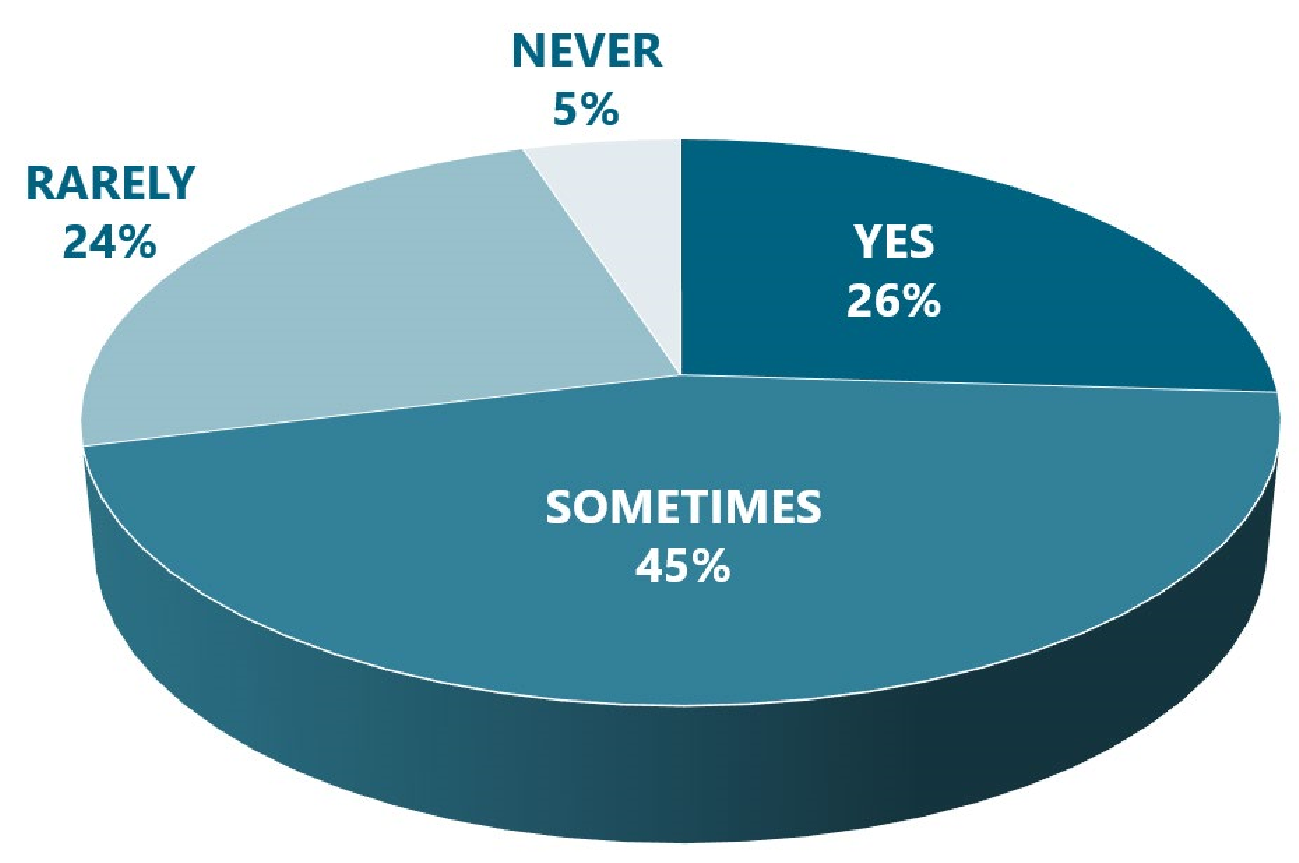
Figure 1: Do your business managers get the operational facts they need from BI reports and dashboards?
What are conversational queries?
Conversational queries can help. This category of business intelligence (BI) uses generative AI to provide real-time search for and retrieval of tabular data through a natural language interface. It complements traditional BI capabilities that measure, predict, and visualize market trends or key performance indicators (KPIs). Conversational queries enable business managers with minimal data expertise to rapidly assemble facts as they make tactical decisions, forecast performance, and brainstorm ideas. They respond to human questions such as the following:
- What was revenue last week for stores in Denver?
- What are the average inventory levels this month to date for our UK warehouses?
- Which customers bought the most books on Cyber Monday?
1 N = 42. LinkedIn poll, March 2024
Conversational queries are one of many analytics use cases for generative AI. GenAI is a type of neural network that trains itself to interpret and generate digital content such as text or audio. Much of the current GenAI excitement centers on the language model (LM), which predicts content – often strings of words – after learning how words relate to one another in an existing corpus of similar content.
LMs such as Chat-GPT from OpenAI or Gemini from Google help knowledge workers of all types improve their productivity. And now conversational queries help knowledge workers consume data, using either dedicated tools such as Quaeris or GenAI features within BI platforms such as Tableau. Various operational applications also can include conversational queries as part of embedded BI modules, for example to generate charts or graphs within a customer portal for financial services. In these and other ways, conversational queries will become a standard aspect of modern analytics.
The BI community, including managers, is especially excited about the ability to query data without writing SQL. In a recent survey by BARC and Eckerson Group, 59% of 214 data leaders and practitioners ranked natural-language queries as the top GenAI capability that their company will use to consume BI outputs. This basic use case is more popular than other GenAI use cases such as generating visualizations or interpreting predictive models.

Figure 2: Which GenAI features and capabilities will business intelligence and analytics users within your organization leverage to consume BIA content?2
2 N = 214. BARC and Eckerson Group, January 2024
State of business intelligence
To understand the role and value of conversational queries, let’s assess the state of business intelligence (BI) today. We start by considering the two stakeholders that consume BI: Power users and business managers.

- Power users are BI experts such as data analysts and data scientists that prepare, query, and interpret data, then create visual outputs such as reports, charts, and dashboards. They deliver these outputs to various business managers to assist in decision making. Swamped with requests, power users need BI tools to improve their productivity.

- Business managers are experts in business domains – perhaps a function such as finance or an industry such as manufacturing – that consume BI outputs, most often from power users. These managers review scheduled reports, consult dashboards, and ask various adhoc questions. They crave self-service capabilities so they can answer their own questions.
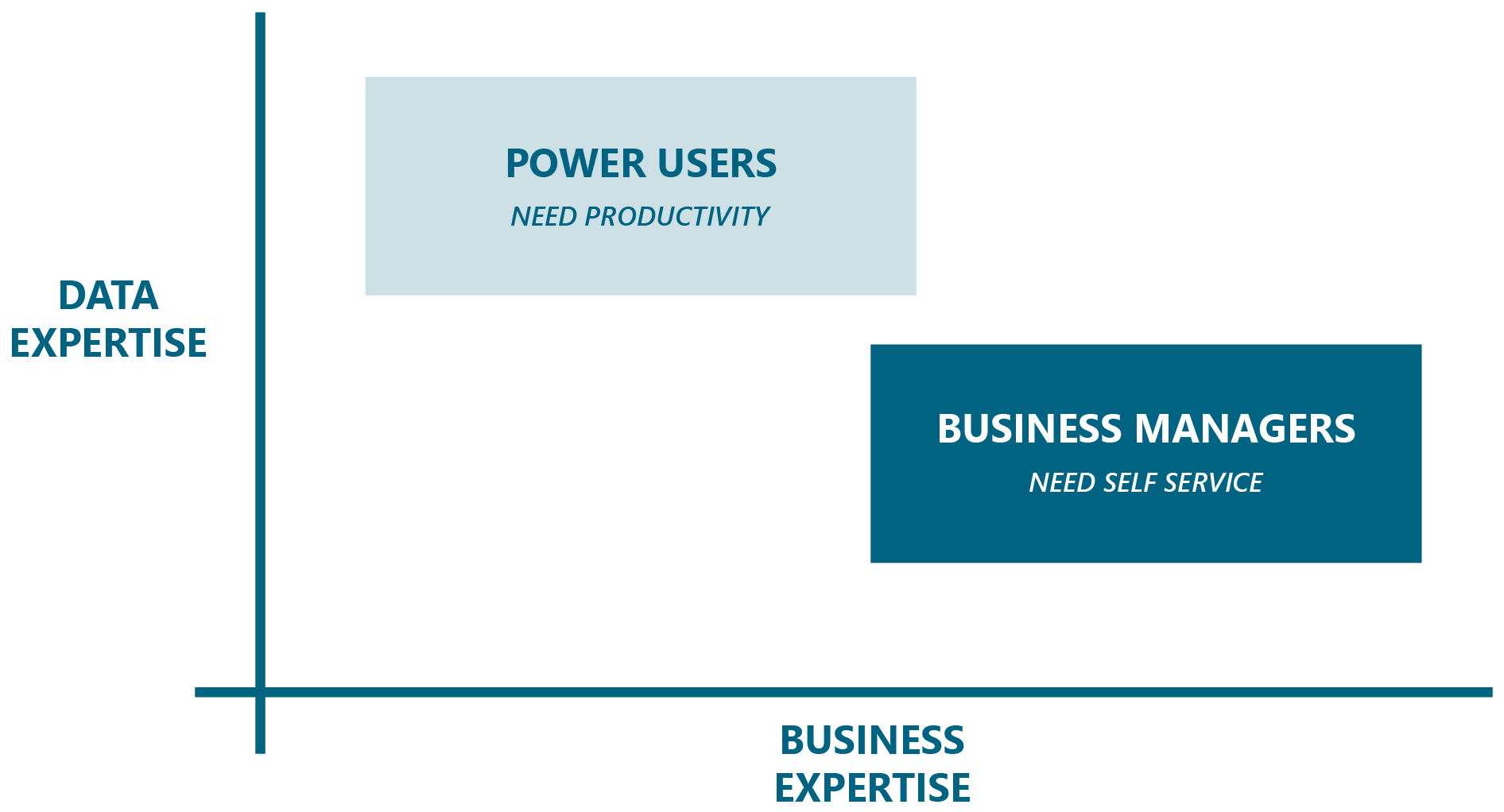
Figure 3: Power users vs. business managers
With these factors in mind, it’s no surprise that business managers express optimism about the potential benefits of GenAI. The BARC/Eckerson Group survey showed that 77% of business managers believe GenAI will improve the use of BI in their company to a moderate, high, or very high degree.
This contrasts with power users, 90% of whom believe the improvements will be moderate to low or very low. The implication: Business managers are shaping up as the most enthusiastic adopters of GenAI use cases for BI – such as conversational queries.
| LOW TO VERY LOW | MODERATE | HIGH TO VERY HIGH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BUSINESS MANAGERS | 22% | 33% | 44% |
| POWER USERS | 40% | 50% | 10% |
Figure 4: To what degree will GenAI improve the use of business intelligence and analytics in your organization in the next 12-18 months? (by role) (n=208)3
How do conversational queries work?
Conversational query tools enable humans to ask questions, find answers, and interpret what those answers mean. Here is the process.
- Ask. The business manager types or dictates their question into a natural language interface such as a chatbot using a browser window or mobile application. A GenAI language model determines the intent of the question, then generates one or more SQL queries to find data relating to that question
- Find. The conversational query tool executes the SQL queries on the company’s domainspecific datasets within a data warehouse or other sources such as SaaS applications and relational databases. The language model reviews the query results and generates a response to the user’s question.
- Interpret. The conversational query tool delivers the response, including the facts retrieved and a description of their meaning in the context of the question. This interpretation stage has three steps.
- The user reviews the response, parses what it means, compares it to other sources, and socializes it with colleagues.
- They explore & ask adjacent questions avenues of research based on their intuition, team discussions, or recommendations from the conversational query tool itself.
- They decide & act. Satisfied they have the right facts and insights, the user makes the decision to buy that component, adjust that price, and so on. Based on the business outcome of that action, they learn and start the iterative cycle again.
3 N = 208. BARC and Eckerson Group, January 2024
Why should companies consider conversational query tools?
Three familiar trends create inexorable demand for BI self-service. First is digital transformation. As companies digitize their operations, they create streams of transactions, logs, and other data that hold potential insights on customer interactions or other aspects of their business. Second, companies continue to democratize access to their data. Business managers, from individual contributors up to executives, need fast and accurate data to make smart decisions. Digital transformation and data democratization contribute to the third trend: Demand for real-time data. Businesses need instant visibility into their operations to meet the needs of impatient and demanding customers. Together these trends support the case for companies to invest in BI innovations such as conversational query tools.
Use case
Use cases for conversational queries cover a broad spectrum given the popularity of digital transformation and data democratization across many functions. Let’s consider an example use case for a chain of automotive dealerships. Their operations team needs to identify ways to reduce the operating costs of its maintenance and repair services. During a daylong meeting they review their standard reports and dashboards, then brainstorm options for streamlining. This leads to a series of rapid-fire questions, which a team member poses to her conversational query tool. And the query tool might even suggest adjacent questions.
Here is an example.
| Original Question | Suggested Adjacent Questions |
|---|---|
| What were monthly repair volumes each month over the last year? |
|
| Which service personnel performed those repairs? |
|
| What replacement parts did those jobs require? |
|
Answering these questions in real-time enables the operations team members to accelerate data exploration, testing and validation of their ideas. They build three specific cost-cutting measures based on evidence of historical practices that inflated spending. As they share this proposal with executives, they use their conversational query tools to address additional questions on a real-time basis. This process enables the team to build, propose, and implement its cost-cutting measures in less time and with higher confidence in the outcome.
Conclusion
Configured and implemented well, conversational query tools enable various business managers to enrich tacit knowledge with hard, real-time data. By summoning the right facts without waiting on BI power users, these business managers can support a variety of use cases for teams spanning finance, operations, marketing, and customer service. They can reduce time to value and respond to market changes in a more agile fashion. They also can make fewer demands of BI teams and free them up to tackle more strategic work, for example to collaborate with data scientists and incorporate AI/ML models into their reporting.
BARC recommends that data and business leaders take the following steps to understand and capitalize on this opportunity for their organization.
- Gather the data requirements of business managers to run operations and support strategic initiatives. Do your leading business managers have the data they need when they need it? What specific data gaps do they perceive?
- Scope whether and how your BI teams meet these requirements today. Do existing reports and dashboards contain the necessary data, and do they reach the business managers that need it? The answer to both these questions is likely to be “no,” or “partially.”
- Evaluate the ability of your existing BI tools, new BI tools, or new conversational query tools to close your identified gap. Create a short list of vendors and test their capabilities as part of product demonstrations and proofs of concept that map to your requirements
About BARC

Dr. Carsten Bange, Founder and CEO of BARC
- BARC (Business Application Research Center) is one of Europeʼs leading analyst firms for business software, focusing on the areas of data, business intelligence (BI) and analytics, enterprise content management (ECM), customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP). Our passion is to help organizations become digital companies of tomorrow. We do this by using technology to rethink the world, trusting databased decisions and optimizing and digitalizing processes. Itʻs about finding the right tools and using them in a way that gives your company the best possible advantage. This unique blend of knowledge, exchange of information and independence distinguishes our services in the areas of research, events and consulting.
Research
Our BARC studies are based on internal market research, software tests and analyst comments, giving you the security to make the right decisions. Our independent research brings market developments into clear focus, puts software and vendors through their paces and gives users a place to express their opinions.
Events
Decision-makers and IT industry leaders come together at BARC events. BARC seminars in small groups, online webinars and conferences with more than 1,000 participants annually all offer inspiration and interactivity. Through exchange with peers and an overview of current trends and market developments, you will receive new impetus to drive your business forward.
Consulting
In confidential expert workshops, coaching and in-house consultations, we transform the needs of your company into future-proof decisions. We provide you with successful, holistic concepts that enable you to use the right information correctly. Our project support covers all stages of the successful use of software.
For more information, visit BARC.com.